The origin of futures trading can be found in a concept called forward contracts. With a forward contract, two parties agreed to sell an amount of an asset for a predetermined amount of money at a specific time in the future. Let’s take a look at an example to illustrate:
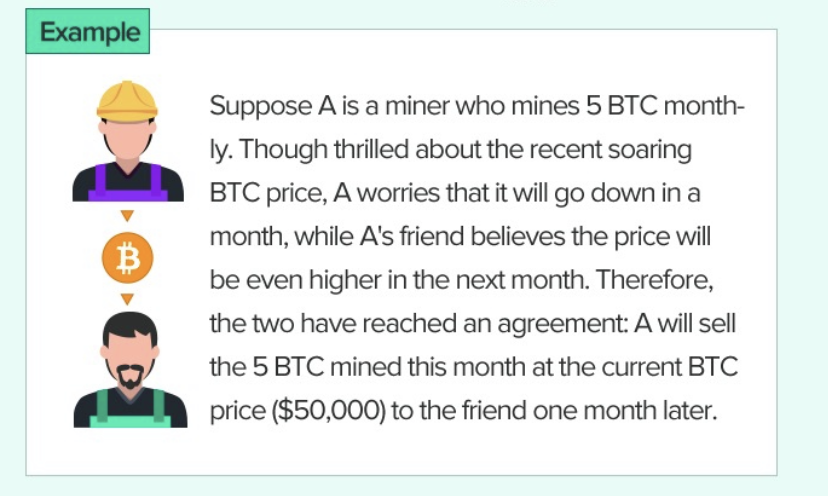
Each forward trade includes:
A future date for the trade/delivery, e.g. “one month later”
An execution/delivery price, e.g. “$50,000”
An underlying commodity (can be intangible things like price index), e.g. “BTC”
A futures contract is a derivative traded in the crypto market.
What is a derivative?
In order to understand what futures trading is, it’s important to understand what you’re trading. And with futures, you’re dealing with derivatives. A derivative is a securitized contract that derives its value from an underlying asset, such as a stock, bond, physical asset or cryptocurrency. And as you would guess, when the assets value changes, so does the price of the derivative.
Different types of futures contracts
We can divide futures contracts into delivery- or fixed term- contracts and perpetual contracts.
Delivery contract: there is a pre-specified delivery date. This is often week- month- or year-based.
Perpetual contract: this contract is available for trading permanently as there is no fixed delivery date, hence the term “perpetual“.
So why use one over the other? Perpetual contracts have no specified delivery date, and can be held open indefinitely. This gives traders more flexibility and the ability to exit their trades when they choose. Interestingly, in the crypto world, traders often opt for this option because they can earn passively through funding fees. These contracts have to be manually closed
But what about fixed-term contracts? Since these more traditional futures contracts DO have an execution (or delivery) date, a trader can “bet” on the price of an asset an make an informed wager with a more definable profit.
The Benefits of Futures Trading
Futures contracts allow traders to speculate on the price of an asset, meaning they can agree to buy/go long or so/go short on a given asset. And what advantages would this bring to a trader? Let’s go through the possible benefits:
Hedge against future risks (“hedging”)
Traders can open futures positions with the same currency and quantity in the opposing direction to their spot investments. This allows traders to diversify their positions and hedge their risk. That is, a trader can open a position against their spot market position.
2. Leverage
Leveraging allows traders to open a large position with a relatively small amount of assets, meaning they can realize larger returns than they otherwise would be able to in a spot market. This of course means that leverage can also amplify losses.
3. Curb the irrationality of the spot market
Not only does futures trading help the individual trader against market volatility and irrationality, it can also prop up the overall market. That is, when an asset’s spot price drastically rises or falls, futures trading can affect the spot market and help push the price back to a reasonable range.
4. Short-selling mechanism
Futures introduce a short-selling mechanism into the market.
Here’s a short example of how this works:

But what are some of the disadvantages?
Future events- While futures can present huge potential upsides, none of us are fortune tellers. That is, although you may be able to bet on future prices by trading futures contracts, you don’t have much control over the future events affecting the underlying assets’ price.
Learning curve to understanding futures- Newer traders might find futures trading a bit more complex, and thus difficult to handle. Whereas a spot market provides instant settlement with relatively simpler mechanisms, futures trading requires more knowledge. As the age-old adage goes, DYOR!
Leverage- While you can open large positions with relatively less assets, you can also realize greater losses as well. This is the inherent risk that comes with using leverage in futures trading.
Expiration dates affecting the market- As an expiry date approaches, it might become more difficult to
find a counterparty willing to fulfill the other side of the futures contract, rendering it useless.
Margin Trading vs. Futures Trading
Another popular method of trading is margin trading. Let’s define how margin and futures trading are similar, and what sets them apart. Both futures trading and margin trading allow traders to amplify their returns with a relatively low amount of cash. They also both allow traders to speculate on price movements by allowing them to buy/go long or so/go short.
Differences:
Concepts:
a. Futures trading: The forward contracts of commodities or standardized financial assets are traded; buyers and sellers buy/deliver an asset at a predetermined date and price. Futures are independent derivative products in the crypto market.
b. Margin trading: Margin defines the asset used as collateral that traders deposit in order to borrow funds. Here, they can borrow much more than they put in, magnifying profits with a smaller amount of capital (which also comes with higher risks); it is important to note that margin trading is an extension of spot trading.
2. User experience:
a. Futures trading: Differentiated trading screen; up to 100x leverage.
b. Margin trading: Since this relies on the spot market, its trading screen is similar to that of the spot market; typically features 1x-5x leverage.
3. Fees:
a. Futures trading: Futures trading fee (low) & funding rate (perpetual contracts only).
b. Margin trading: Spot trading fee & interest charges based on the loan.
3. User action:
a. Futures trading: Two directions; users need to select buy/sell and the leverage when opening a position.
b. Margin trading: Two directions; when opening a position, users need to borrow tokens accordingly depending on the direction (buy or sell)
That wraps it up on futures trading, although we will delve into different parts of this financial instrument, as well as how to go through interacting with Poloniex’s futures trading product in the future, so stay tuned for those articles! In the meantime, if you feel ready, you can sign up and start trading futures today!
And for a limited time we are offering benefits for futures trading: register and open futures through the invitation link, complete any trading amount of futures transactions, and you can get $5-$30 in trial funds.
*Quota is limited to 200 people

was originally published in The Poloniex blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

