Coinbase’s View
At 11:10 PM PST 7/31/2020, Coinbase Blockchain Security was alerted that Coinbase’s ETC nodes were not seeing new blocks at the expected interval. Our investigation found that our nodes had forked in terms of their blockchain state. Coinbase’s internal pruned parity nodes were seeing different blocks than our non-pruned Parity and Geth nodes. This was the first indicator that something was wrong. We concluded that a massive reorg at 10:57 PM PST 7/31 caused the network to fork due to differing node implementations (for more information on the fork, see the network partition section below).
An extremely large reorg is a significant indicator of potential double spends. At this point, Coinbase chose to significantly raise our confirmation count requirement. This ensured that no double spend transactions were credited on the Coinbase platform.
Two open questions followed: First, did the reorg actually contain any double spends? Second, given the network partition, how does Coinbase ensure we’re on the right chain?
In order to answer the first question, we compared the orphaned chain and the new chain that caused the reorg. We found ~$5.8 million double spent across 53 orphaned transactions. Coinbase was not targeted by these attacks.
Our next focus was understanding the ETC network partition. We discovered pruned Parity nodes would ignore blocks past a certain height. Because the massive reorg tried to orphan blocks beyond this threshold, pruned Parity nodes considered the reorg invalid. Note that the rest of the network chose to follow the reorg, which caused the network to partition. After observing each side of the network partition, Coinbase began following the canonical main chain (I.e. the non-pruned Parity chain which includes the double spend attack).
On the night of August 5th, Blockchain Security got another alert that a massive reorg occurred. Because pruned parity nodes were no longer being operated, there was no network partition akin to the first reorg. Therefore, the singular question was whether Coinbase was the victim of this attack. Doing a similar analysis as above, we confirmed ETC was attacked again, this time for around $3.2 million across nine orphaned transactions. Once again, we found that Coinbase was not the victim for any of the orphaned transactions.
As an additional precaution, we raised the confirmation count further to ensure the security of our customer funds. Note that this is not the first time ETC was successfully double spent. Refer to our previous blog post for details about the previous attack.
While ETC looks to have stabilized in recent days, we continue to monitor for any further ETC turbulence.
Technical Analysis
Nonce-based Double Spends
In this ETC attack, we discovered an interesting pattern used to execute the double spends. We discuss one example of the attacker’s double spend strategy below:
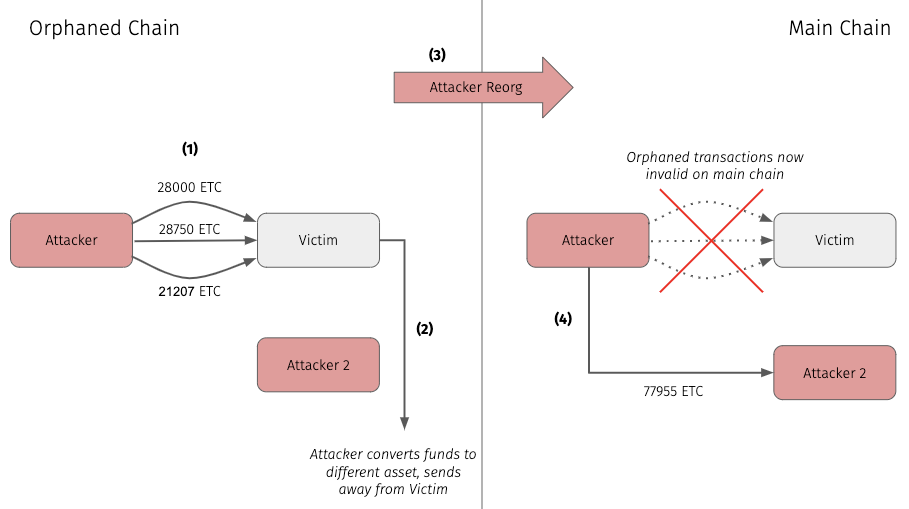
Attack Pattern:
Attacker sends a large amount of ETC through multiple transactions to victim
Using the victim service, attacker converts ETC to some other currency then moves funds off platform
Attacker reorgs the blockchain “erasing” the transactions from step 1
Now the attacker has access to their original ETC. They move the sum of their funds to another address they control using one large transaction. This is necessary in order to invalidate any replays of the orphaned transactions
End state: The attacker now controls some amount of a non-ETC asset that they exfiltrated from the victim, while also maintaining control of the original ETC.
Interestingly, by using this incremental nonce based technique, each orphaned transaction moved less than 30,000 ETC (~$200,000). We believe that the attacker used these incremental orphaned transactions due to some value-based rate limitation of the victim. For example, a victim exchange may have had a feature preventing a user from receiving greater than x amount of ETC in a single deposit.
The following is the actual ETC data for this double spend:
https://medium.com/media/ed6bc6eb10e104c107e0aa4b719c483d/href
Here, we find three transactions that occurred on the orphaned chain. The sender (i.e. attacker) and receiver (i.e. victim) address are consistent across all three transactions. As mentioned above, the amount transferred in each transaction hovers around ~$200,000. Additionally, the latter two transactions have incremented nonces when compared to the previous transaction. This is expected based on how account nonces work.
The key point is that on the main chain, neither of the latter two transactions are valid so long as the attacker account doesn’t hold enough funds to cover the transfers. In the main chain, we find one large double spend transaction from the attacker address, as opposed to three separate double spend transactions, one for each of the above orphaned transactions.
https://medium.com/media/d2fc3cca74e2769802378f3a96dc2272/href
Note that the transfer value for this large transaction is equal to the sum of the values of the three orphaned transactions. This ensures all three orphaned transactions are invalid on the main chain.
Pruned Parity Node Network Partition
Beyond the normal 51% attack double spend attack pattern, a second interesting case arose due to this incident: The Parity OpenEthereum client, when configured in pruned mode, will choose to ignore any blocks past a certain height as “ancient” and consider these blocks invalid.
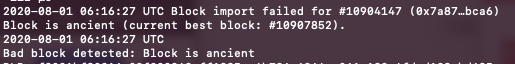
Therefore, pruned Parity OpenEthereum clients ignored the reorg and continued mining their own separate chain. As mentioned above, we call this the orphaned chain. The invalidity of the reorg chain caused the network to partition by node and node configurations.
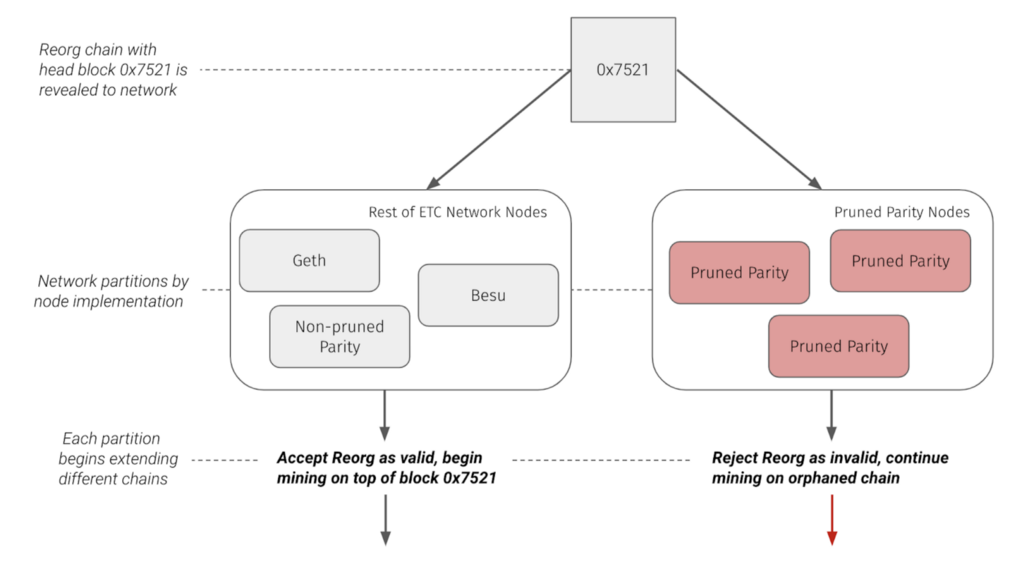
After this partition occurred, miners continued to mine on both the pruned Parity chain as well as the main chain that the rest of the network followed.
For clarity, note that the pruned Parity nodes’ current state is equivalent to the unpruned Parity, and Geth node’s state before they were reorged. Requesting a block at a certain height within the reorg returns the orphaned block from the pruned Parity node while the unpruned Parity node returns the attacker block. The orphaned block received from the unpruned node used to be part of the unpruned Parity node’s state, however the orphaned block was reorged out of the unpruned node’s view.
Node operators that continued to run pruned parity nodes maintained and extended the orphaned chain. Until these operators resynced their pruned parity nodes or switched to a different node type, the networked remained partitioned. Coinbase strongly recommends switching to a supported node (eg. Geth).
Reorgs
According to Coinbase non-pruned node logs, there was an extremely large reorg that started at block height 10904147 until block height 10907434. At the time of the attack, the main (i.e. attack) chain had height 10907434 while the orphaned chain had height of 10907836. The common ancestor block between the orphaned and main chain is at height 10904146. This means the reorg orphaned 3692, and added 3287 new blocks. Note that while the attack chain had a lower height, because it had a higher difficulty it superseded and overtook the orphaned chain as the canonical chain for ETC. Assuming a block time of 15 seconds, the attacker had to mine with majority hashpower for around 13.7 hours to execute this attack.
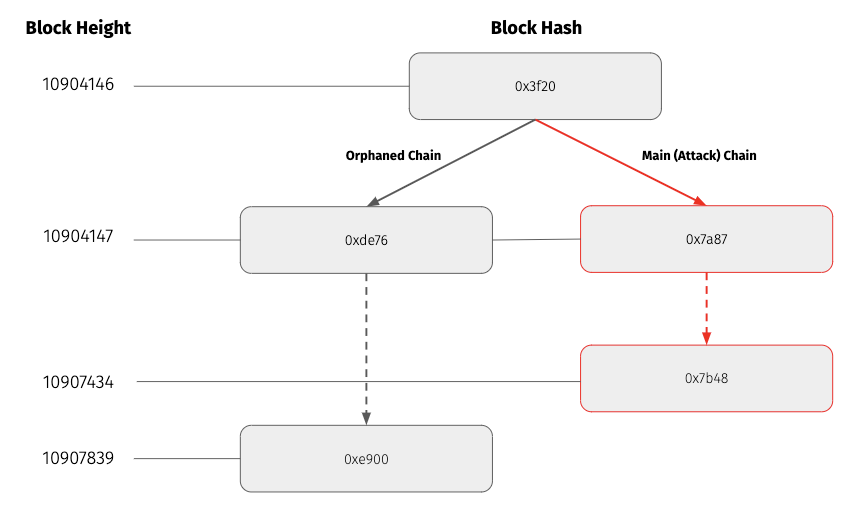
The pruned nodes ignored this reorg while the un-pruned nodes accepted this reorg as valid. See the Network Partition section above for more information.
Our analysis shows 15 double spending transaction pairs and 38 nonce-based orphaned transactions in the chain reorg. None of the double spends affected Coinbase.
On 8/5/2020, ETC saw a second massive reorg on the main chain.
At the time of the reorg, the orphaned chain head block was 0x9555 at height 10939866. After the reorg, the main (i.e. attack) chain head block was 0x7521 at height 10939975. The common ancestor block between the orphaned and main chain is at height 10935622. The reorg orphaned 4244 blocks, while the attack chain contained 4353 blocks. Assuming a block time of 15 seconds, the attacker had to mine with majority hashpower for around 18.1 hours to execute this attack.
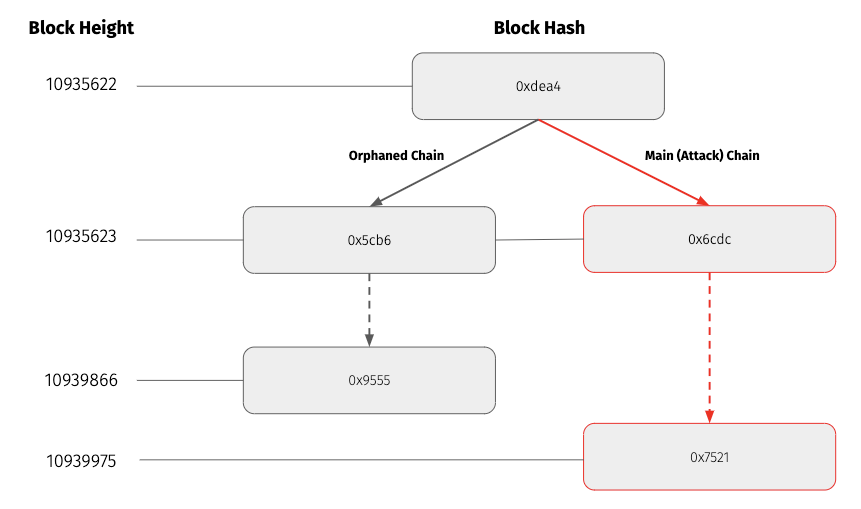
Blockchain Security performed the same analysis as above on this reorg and found 7 double spend transaction pairs and an additional 2 orphaned transactions sent to the victims address. Once again none of these double spends affected Coinbase.
Double spends
In the first series of double spend transactions, we found that around $5.8 million was double spent. There were five unique addresses sending large volume double spend transactions to five unique victim addresses. The attacker and victim addresses mapped one to one.
After examining the to and from addresses, Blockchain Security came to the conclusion that none of these double spends affected Coinbase :
https://medium.com/media/b7c25b19b82c9f85575bc8318b2a2290/href
In the second series of double spends, we found that around $3.2 million was double spent. This time around, there was exactly one target victim address: 0x38cd54fc7b1fe7994355fce1d75c9c4bd7335a46. Additionally, the amount double spent per transaction had a much higher variance, between ~$97,000 and up to ~$1.08 million. We found that in the second attack, the attacker tended to not split up the orphaned transactions, meaning the orphaned and attack transactions generally mapped one to one. The one exception was the particular attacker address 0xa56cfaef495a45f17f44fd0b2d85e0fe63b9ba7d which sent three orphaned transactions.
https://medium.com/media/bf627760c05300306b25678647315060/href
It should be noted that in the first reorg, our analysis also found a number of other small double spends, on the order of ~10 dollars. We believe these to be non-malicious users interacting with the blockchain during the reorg resulting in non-malicious double spends.
Next Steps
Coinbase takes security very seriously. As part of that commitment, we monitor blockchains for activity that could be harmful to our customers and take prompt action to safeguard funds. We want to emphasize to customers that Coinbase strives to be the most trusted and safest place to buy, sell, or store cryptocurrency.
The following is Coinbase’s complete set of data regarding the two double spend attacks:
https://medium.com/media/6c508efda229984502967a31be8f7d9b/href https://medium.com/media/6b0af22382c1767c7dc6a76d315a6b20/href https://medium.com/media/adef7a773866b58d4a62d56b988b7701/href https://medium.com/media/89823e8e066981d2d02efce2f3bc2f4b/href
This website contains links to third-party websites or other content for information purposes only (“Third-Party Sites”). The Third-Party Sites are not under the control of Coinbase, Inc., and its affiliates (“Coinbase”), and Coinbase is not responsible for the content of any Third-Party Site, including without limitation any link contained in a Third-Party Site, or any changes or updates to a Third-Party Site. Coinbase is not responsible for webcasting or any other form of transmission received from any Third-Party Site. Coinbase is providing these links to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement, approval or recommendation by Coinbase of the site or any association with its operators.
While care and consideration has been taken in the creation of the material on this website, we do not warrant, represent or guarantee that the material published on this website is in all respects accurate, complete and current. To the extent permitted by law, we exclude any liability, including any liability for negligence, for any loss or damage arising from reliance on material on this website
All images provided herein are by Coinbase.
was originally published in The Coinbase Blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.

