Introduction to Stablecoins
What are Stablecoins and how did they come about?
The financial world was completely disrupted by the advent of cryptocurrencies, as well as their first manifestation in 2009 - Bitcoin, by the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto.
Since then many different forms of cryptocurrencies came into existence. One general drawback or benefit (depending on how you think about it) is that the majority of cryptocurrencies have a history of having highly volatile prices.
This means that the market price of cryptocurrencies fluctuates greatly and that it is near impossible to predict trends in the market. Although these big price fluctuations can work in favour of cryptocurrency traders, the lack of stability makes it very difficult for businesses to consider it an effective or safe payment option.
For this specific reason, a new form of cryptocurrency was invented, known as “ the stablecoin.”
Stablecoins remove volatility from the market by pegging the price of a stablecoin to another stable asset. This can be a real world currency or a rare metal.
Although, the exact mechanics behind each stablecoin can be very complex, the general idea is really simple; a cryptocurrency coin meant to hold a stable value. Stablecoins can essentially be seen as dollar substitutes which allows one to get out of a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin on an exchange that doesn't deal in US dollars.
This enables you to get into cryptocurrency with a stable price and facilitates the act of trading cryptocurrencies back into cash.
Today, there are several different stablecoins in circulation, all of which are unique but work in similar ways. Stablecoins hold collateral equal to, or that exceeds, the total value of the stablecoin.
The value and type of collateral used depends on which of the three types of stablecoin it is.The three different categories of stablecoin are; Fiat-Collateralized, Crypto-Collateralized and Uncollateralized.
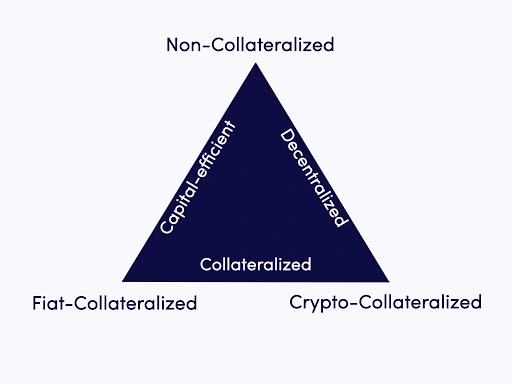
Fiat-Collateralized
The first stable coin is Fiat-Collateralized stablecoins. These are cryptocurrencies that are backed by a real world currency, usually on a one to one basis. This makes them more of a digital representation of a real currency, rather than a just pegged currency.
An example of a Fiat-Collateralized stablecoin is Tether, the first and most popular crypto stablecoin.
One of the main characteristics of these stable coins is that for every digital coin, there is an equivalent fiat money held as collateral in a central bank. For example, for every Tether token (USDT), there is $ 1 US dollar in reserve.
However, despite being pegged to the US dollar, USDT is rarely exactly $1 US dollar. The lowest value it hit was $0.88 in 2018 and the highest the value was $1.06 in 2017. The use of central banks in the process means that these stablecoins are centralized and often can lack transparency.
Crypto-Collateralized
Crypto-Collateralized stablecoins are similar to Fiat-Collateralized stablecoins in the way that they hold collateral for the stablecoin. However, as suggested by the name, crypto-collateralized coins are backed by reserves of another cryptocurrency and therefore intend to remove the dependency on fiat currencies entirely.
To tackle the issue of volatility among cryptocurrencies, for every $1 dollar of stablecoin, there needs to be more than $1 dollar in cryptocurrency in reserve. This is done to protect the value of the stable token in case of downward pressure on the market.
The more volatile the cryptocurrency used as collateral, the more reserve is needed as collateral. A good example of a Crypto-Collateralized currency is Maker DAO which was founded in 2014 but has only been traded since 2017.
These stablecoins have a model that is more decentralized and transparent than the Fiat stablecoins.
Non-Collateralized
Non-Collateralized stablecoins are not tied to any cryptocurrency. They do this by modelling a smart contract as a central bank with the single mandate of issuing coins that will trade at $1 dollar.
As stated in the name, these stable coins do not hold any collateral and therefore are not backed by anything other than the expectation that they will retain a certain value.
Issuing new coins when demand increases allows the cryptocurrency to increase supply and lower the price back to the peg. The stablecoin then also uses bonds to remove coins from circulation when need be.
Anytime the value of the stablecoins drops below $1, shares are offered to speculators at just below $1. These speculators are essentially offered a portion of the future growth of the stablecoin market cap in exchange for providing the capital to peg the currency. Carbon USD or CUSD is an example of Non-Collateralized stablecoins as they control the supply of tokens to ensure the value maintains its stability and thus keeps its peg to the dollar.
The downsides to this type of stablecoin are that the value of the token is based on a promise for future growth and that if demand stops growing, the stablecoin will no longer be pegged.
The Future of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are the fastest growing sector in the cryptocurrency market, making it clear that many people see a big future for stablecoins.
So far, 87% of global central banks are now investigating the possibility of launching their own currency-backed stablecoin. Many large corporations have announced their interest in cryptocurrencies.For example, JP Morgan has just released its own stablecoin token called ‘JPM coin’.
JP Morgan’s aim in developing the coin would be to increase settlement efficiency for its clients. Moreover, rumours have spread recently that facebook has been developing a stablecoin of their own, intended largely to ensure faster and cheaper international transactions.
Will demand for stablecoins increase? It is difficult to say. Many believe that stablecoins have the potential to completely transform our financial institutions in the near future.
However, what is certain is that digital currencies have a much higher chance of becoming a reliable trading asset if they step away from being speculative tools, and that's where stablecoins set themselves apart.

