Back in 2018, when we set out to build the next-generation JVM stack to power our growing business, we set out some goals:
Start small and scale to ride the next Bitcoin bull run
Service customers faster than in the blink of an eye under varying loads
Service customers 24 hours a week, 365 days a year
Stay transparent: when a service is under-performing, clients learn about this, and can immediately react
Then, we quickly learned the fastest human eye-blinkers's performance is roughly 200 milliseconds. Also, apparently there are many fast eye-blinkers who want to jump on the Bitcoin band wagon. As the business goals and the first set of requirements became known, a more refined set of software-engineering goals was identified:
Stick to domain-driven design, identify natural context boundaries
We were not sold on orchestrating tens, possibly hundreds of microservices. Instead, we wanted to start with just one service and add more if the need arose.
Design software with resilience in mind
Each service implementation should have well-understood and testable unhappy path handling. Whenever this path is encountered and the system cannot self-heal, all errors are transparently propagated to a supervisory entity and the faulty instance is removed from the operation. Finally, if there are faults in the system, they don't propagate to other context boundaries and bring our whole operation to a halt.
Avoid heavy frameworks which come with tons of dependencies
Each dependency comes with some hidden cost. One is its potential exposure to security vulnerability. The other is losing control altogether, which means performance-tuning and just keeping our application maintainable, scalable and predictable is a much more difficult job.
H1: Multi-Reactor For The Masses
Enter the Vert.X and its 650 kB of asynchronous, reactive Java framework goodness.
At the core of Vert.x is the principle event-handling. Traditionally, Java applications scaled by encapsulating work-loads on Threads. While in modern multi-core systems, threads are cheap and operating systems are built to support enormous amounts of concurrent workloads, in Java, it is still quite complex to reign in orchestration of threads.
This has partly to do with Javal's memory model (chapter 17.4) when threads have to access shared memory - heap space. Get this wrong and you are in for some pretty frustrating hours of debugging out-of-memory, dead-locks, live-locks and the likes of Java concurrency.
Now imagine we set a number of available threads in the system to a fixed number up-front. We don't create any new threads while running the application and design workload execution to take place on any of these threads. Furthermore, the application instructs the execution layer on what to do by emitting events and by registering handlers ( who does it) which execute in a so-called event loop. When the processing of one event is finished, the next event-handler is called to occupy the underlying thread.
In summary, the life cycle of threads and the entire cost of concurrency management is completely solved by the framework.
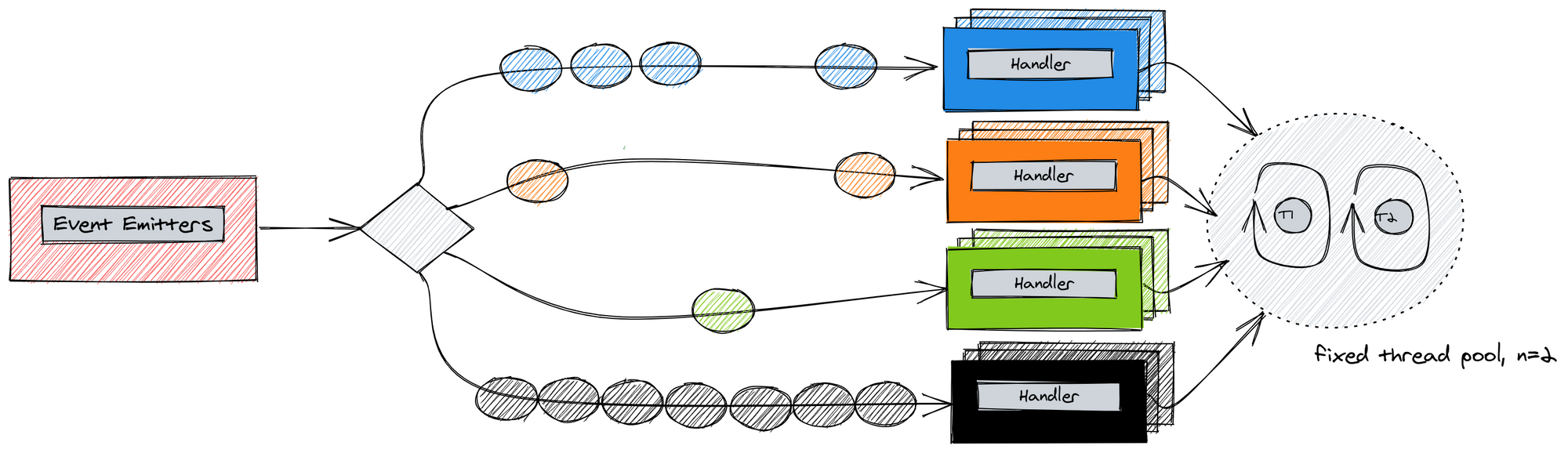
At this point you might think, this is all well and good, but how does it relate to your goals that you set out to achieve? Well, imagine the service you've been commissioned to build is a HTTP server. In case of Vert.X you can seamlessly hook your event handlers to Netty's ChannelHandler (another multi-reactor) and your final setup could look like this:
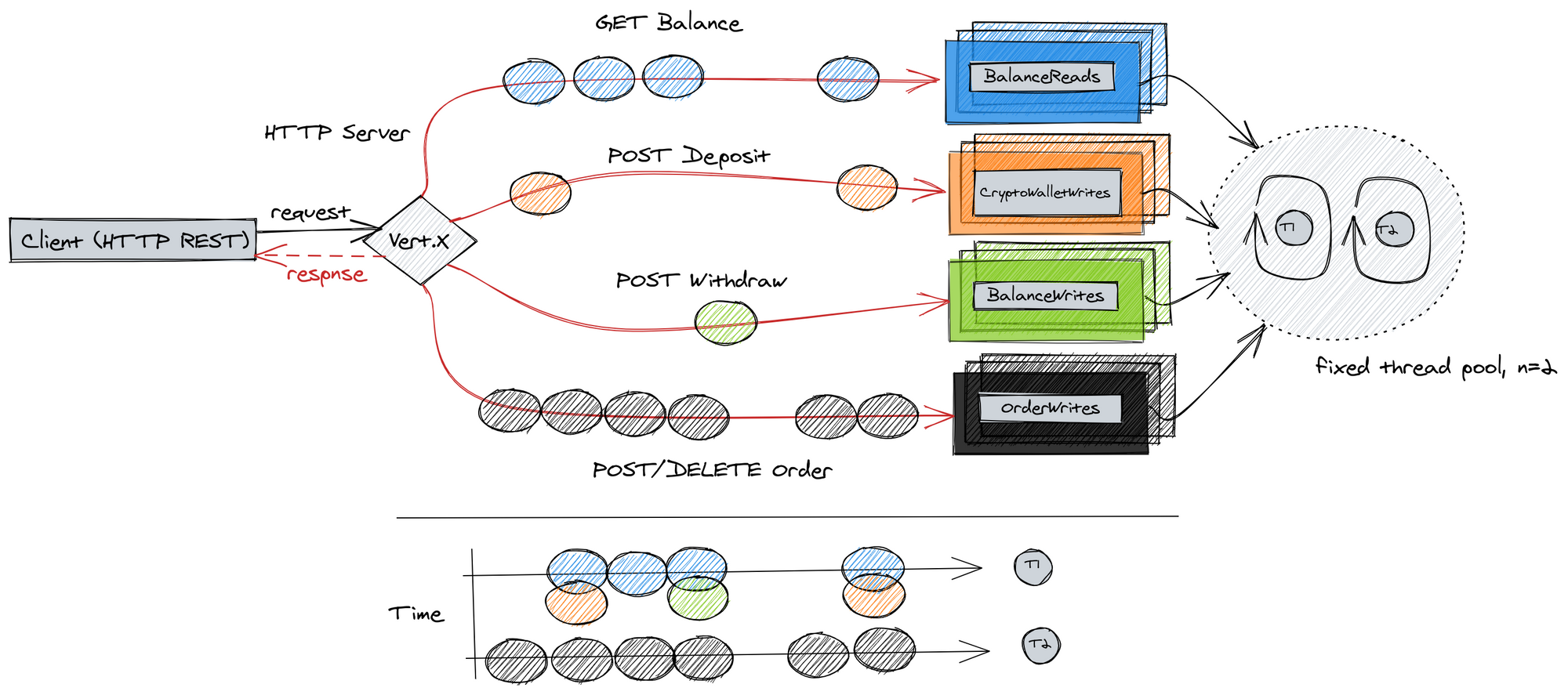
Notice the time axis at the bottom where every slice represents concurrent processing of user requests using registered event handlers. Some requests may be very cheap to complete - fetching current account balance, while others - processing a new client order - may take longer. This means that while one thread is occupied by creating a new order to buy Bitcoin, the other registered event handlers may complete processing requests to deposit or withdraw funds on the other available thread.
Verticles As Context Holders
Verticles are the entry point to Ver.X multi-reactor. Each Verticle is spawned with its own Context which is not visible to other verticles. This forces developers to organise code in a perfect share-nothing encapsulation. Moreover, each context allows for perfect testability of the business logic. Integration to database or message-oriented-middleware which resides in other contexts can be mocked and eventually tested separately.
A good practice for writing verticles is to register an exception handler which nicely aides our goal of resilience by design.
@Override public void start(Promise start) { //do this before anything else context.exceptionHandler(error -> { if(error instanceof FatalError) { escalateAndShutdown(error); } else { log.error("this error is ignored", error); } });
registerServiceHealthCheck();
//complete start-up only when successfully connected to database registerHandlerWhenConnectedToDatabase().setHandler(start.future()); }
and clean up when you're done.
@Override public void stop(Promise stop) { databaseConnectionPool.close().setHandler(stop.future()); }
Since verticles operate with their own share-nothing contexts, it is not possible to facilitate direct method-calls of this sort:
@RequiredConstructor public final class OrderProcessingVerticle extends AbstractVerticle
// never reference another Verticle private final OrderMatchingVerticle matching; // or other context than own private final Context parentContext;
private MatchResult match(Order order) { return matching.handle(order); }
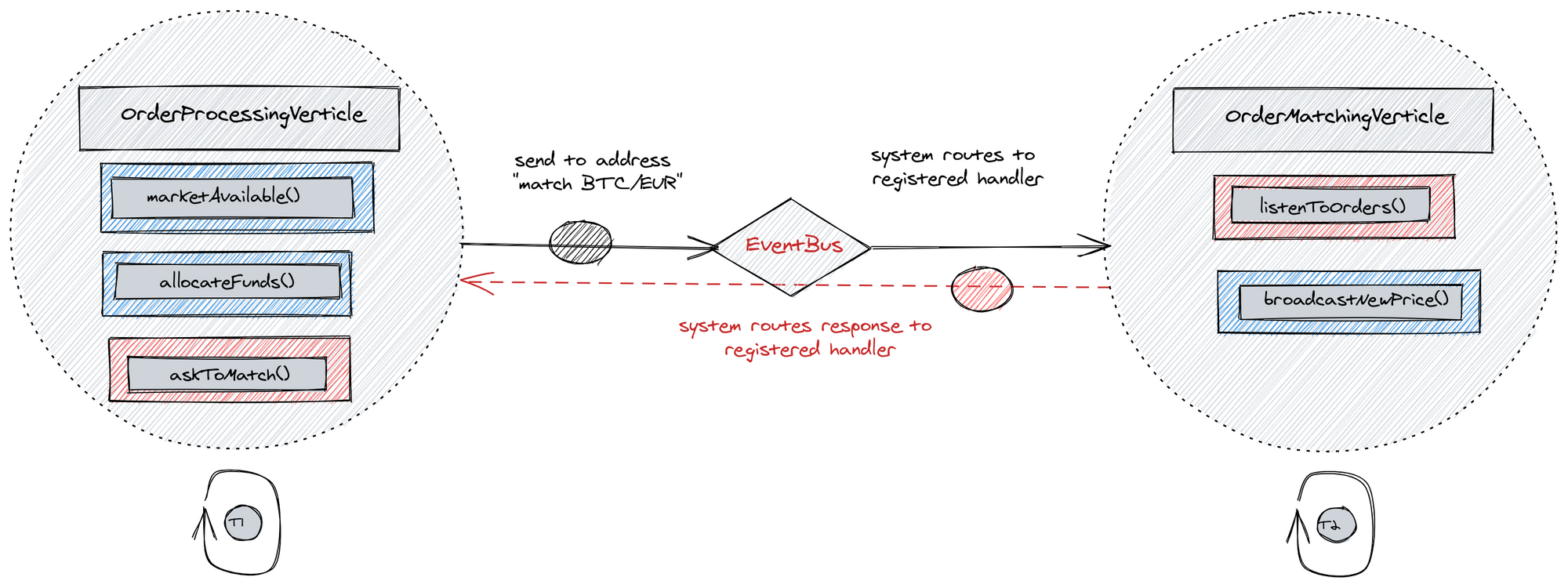
Instead, if one verticle wishes to communicate to another it does so by passing a message over EventBus to a specific address.
Using ask:
Using broadcast:
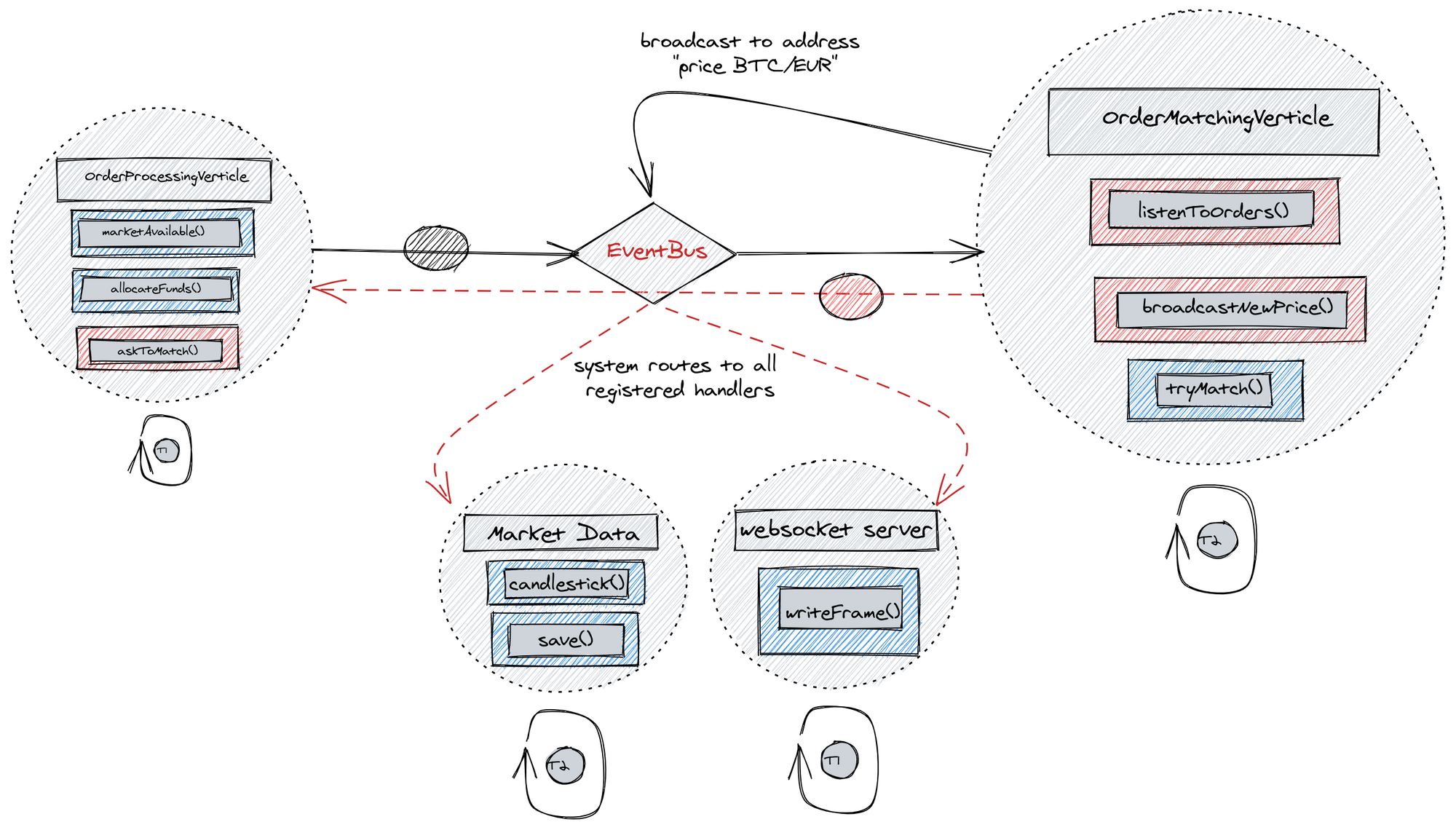
By chaining event handlers which may operate in many fully independent contexts, Vert.X framework provides building blocks for creating a complex and performant system which at the same time allows for clean architecture. We argue such a reactive system is easier to reason about than its many alternatives and leaves room to grow your business in times of emergent requirements.
In future posts, we will look at how we solved service encapsulation and why we at Bitpanda Pro love Apache Kafka.

